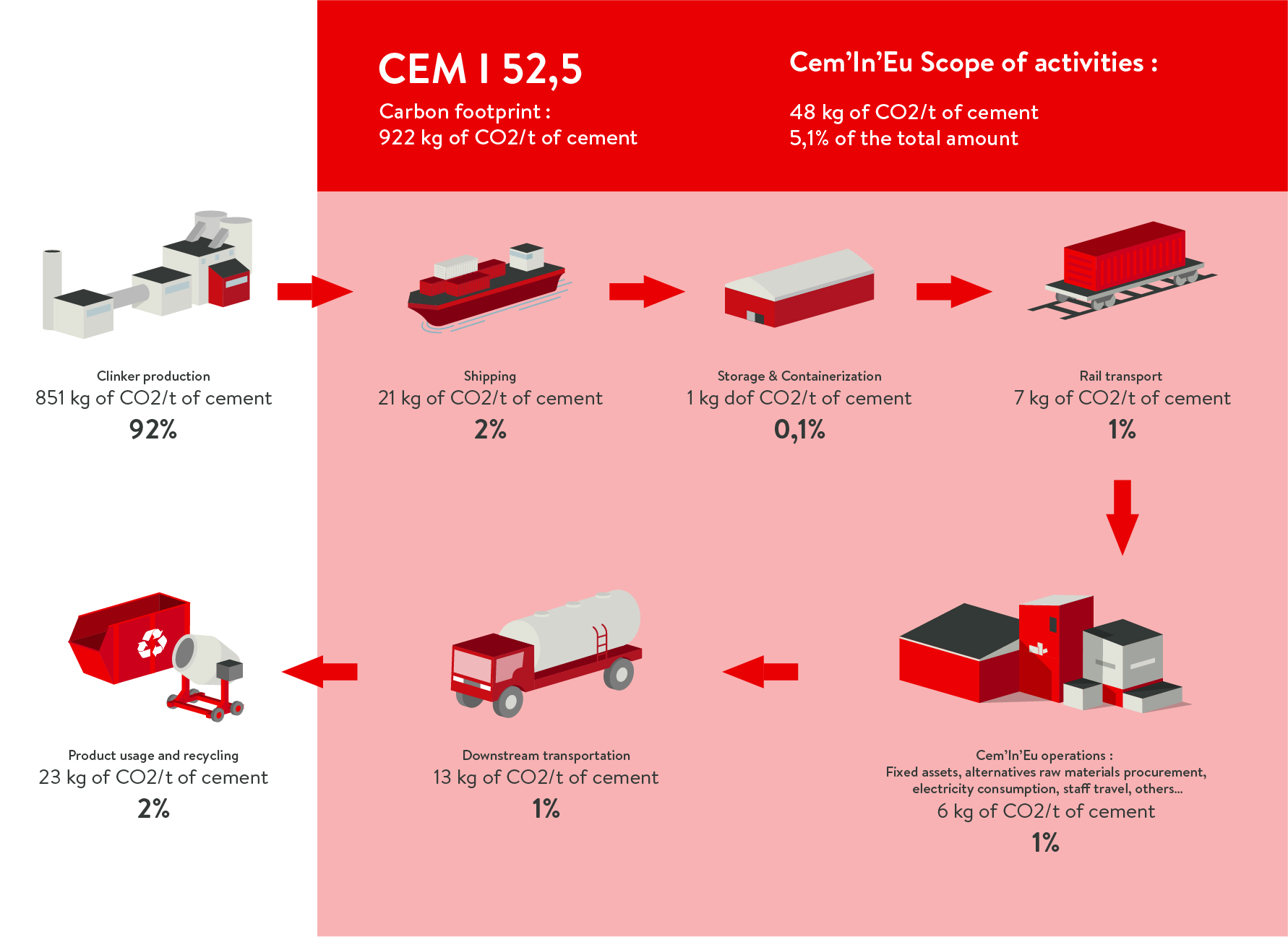
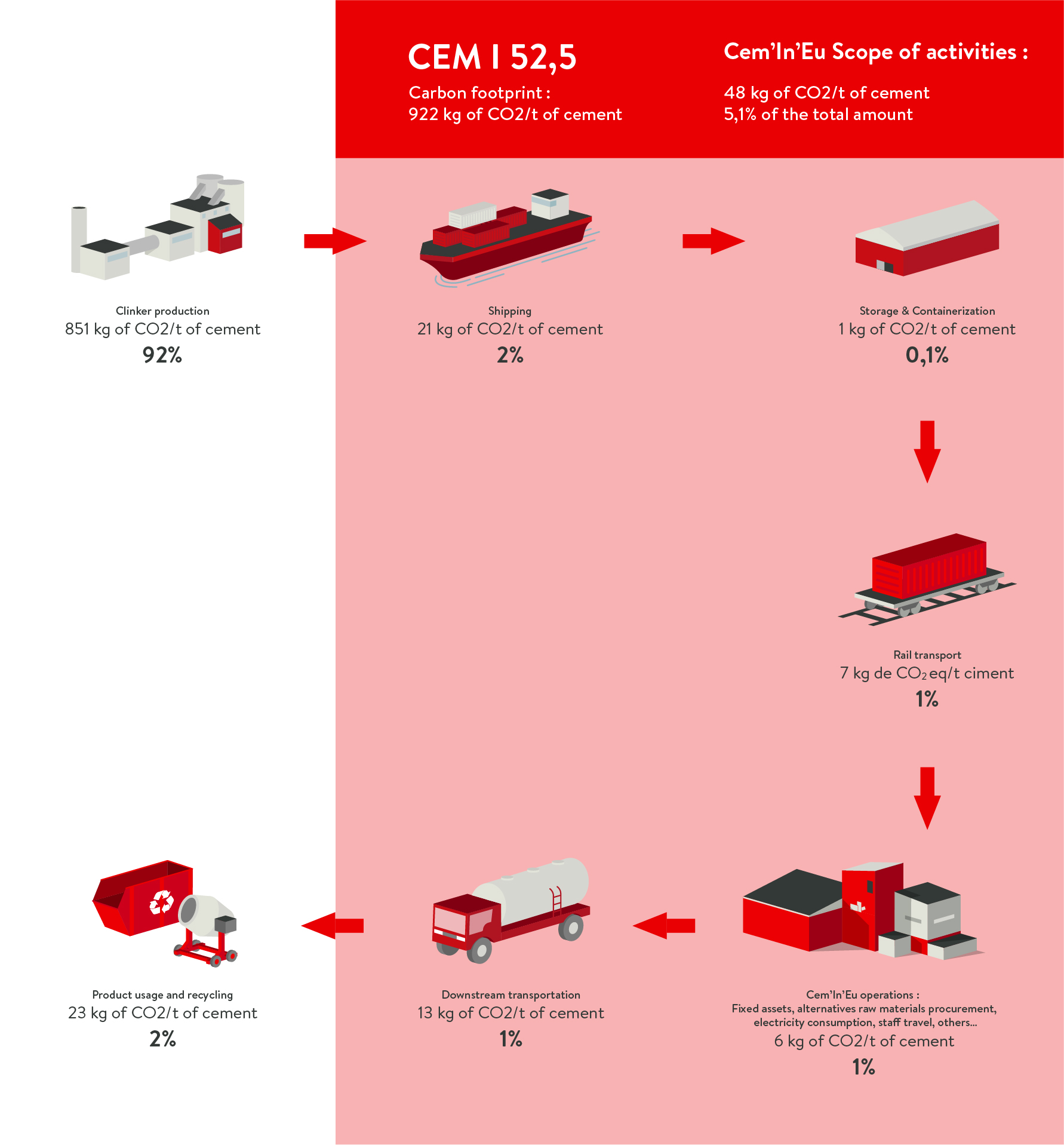
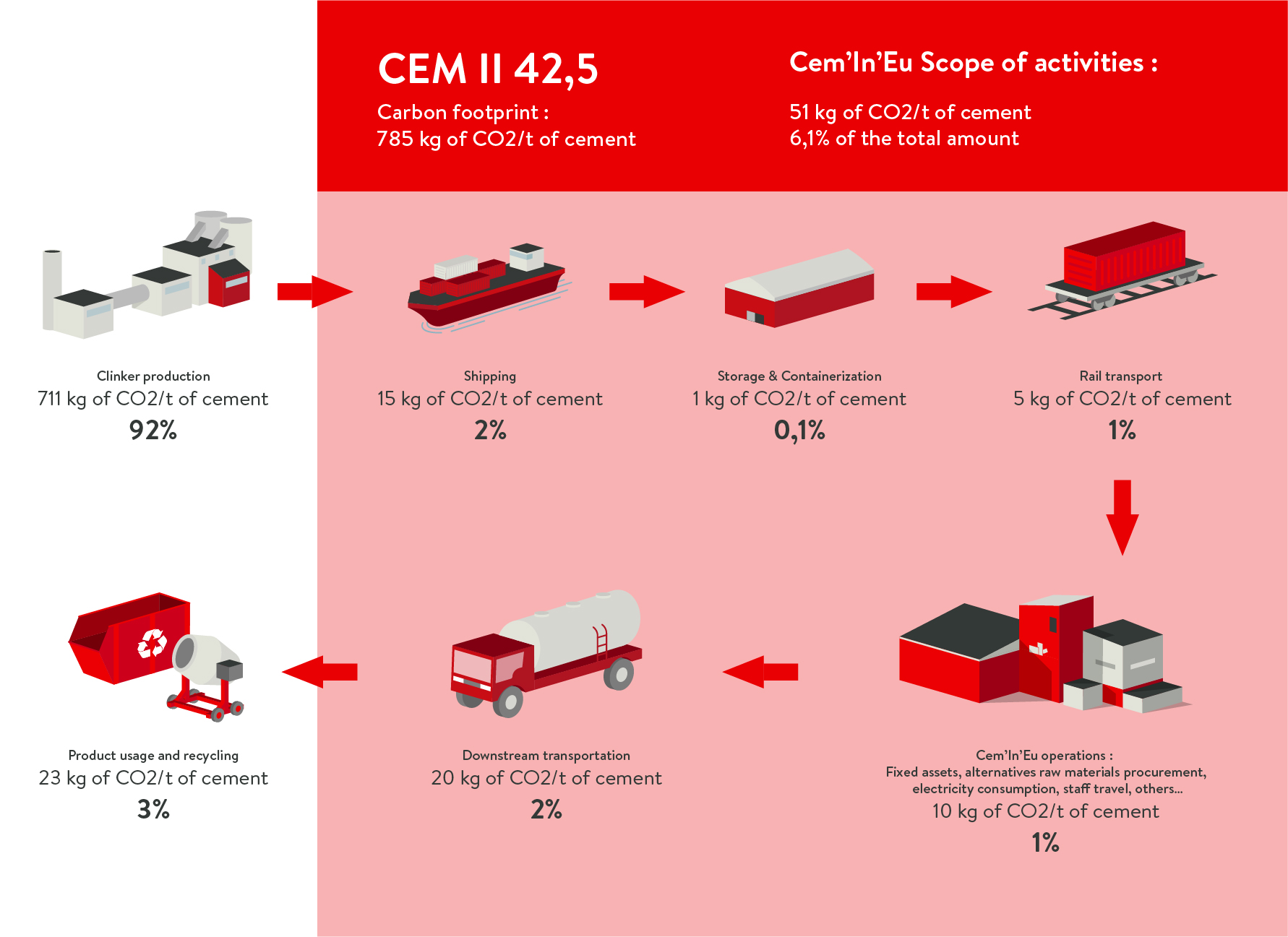
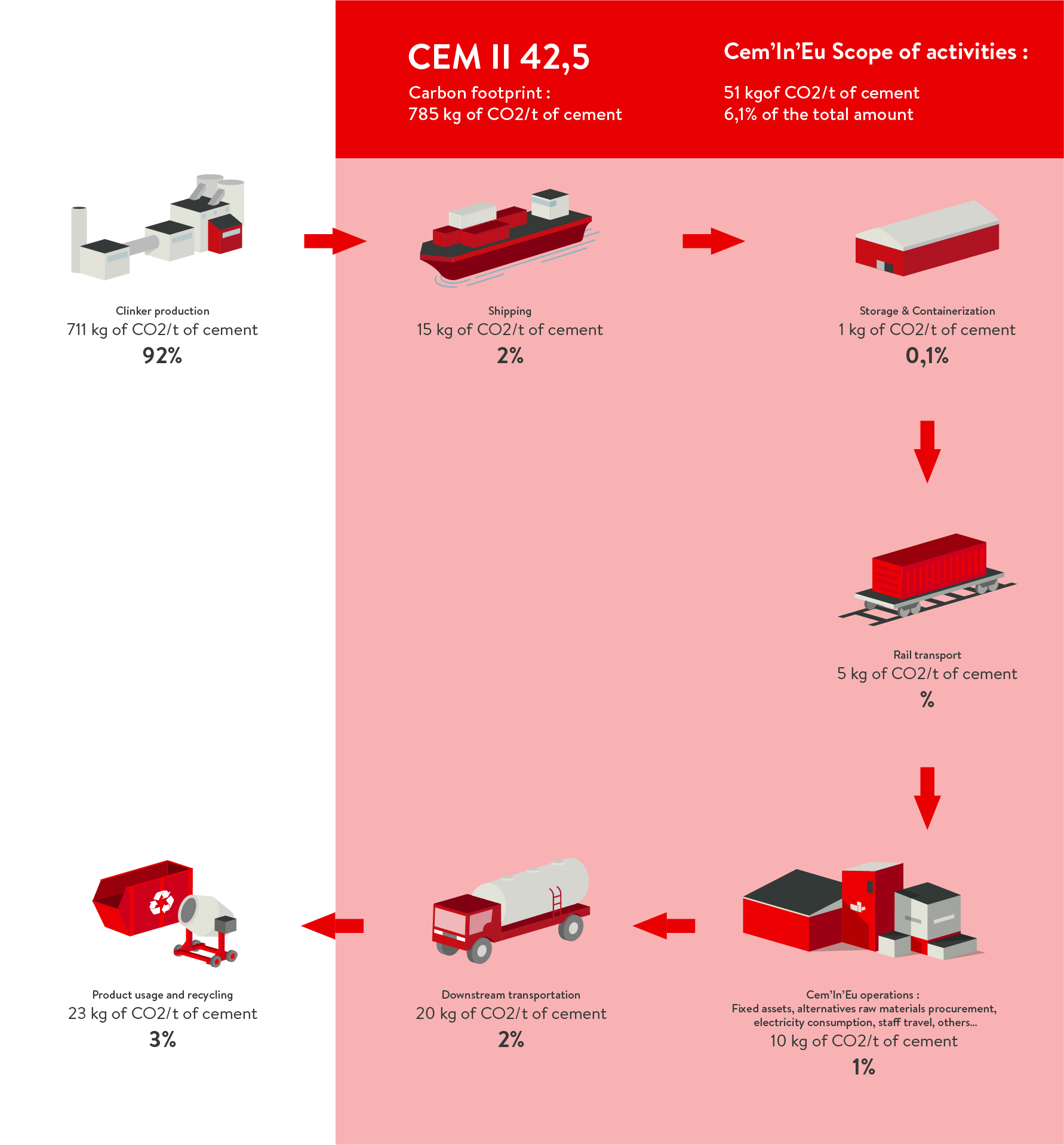
The carbon footprint of Cem’In’Eu products
This calculation is taken from the 2019 carbon estimation entrusted to the Carbone 4 company.

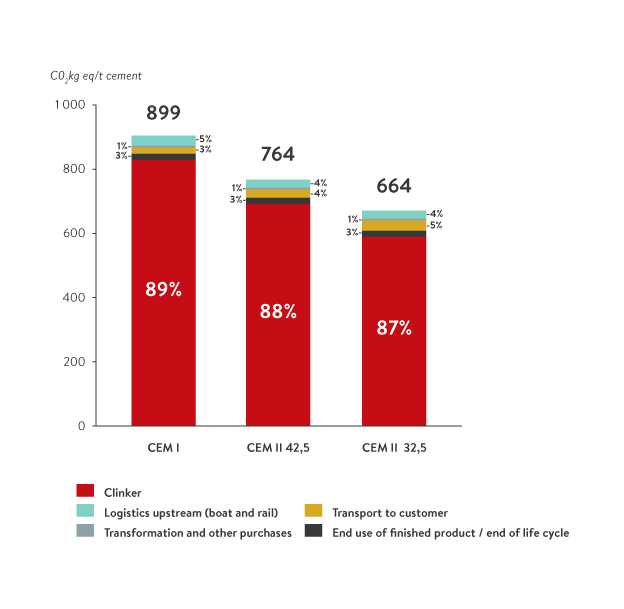
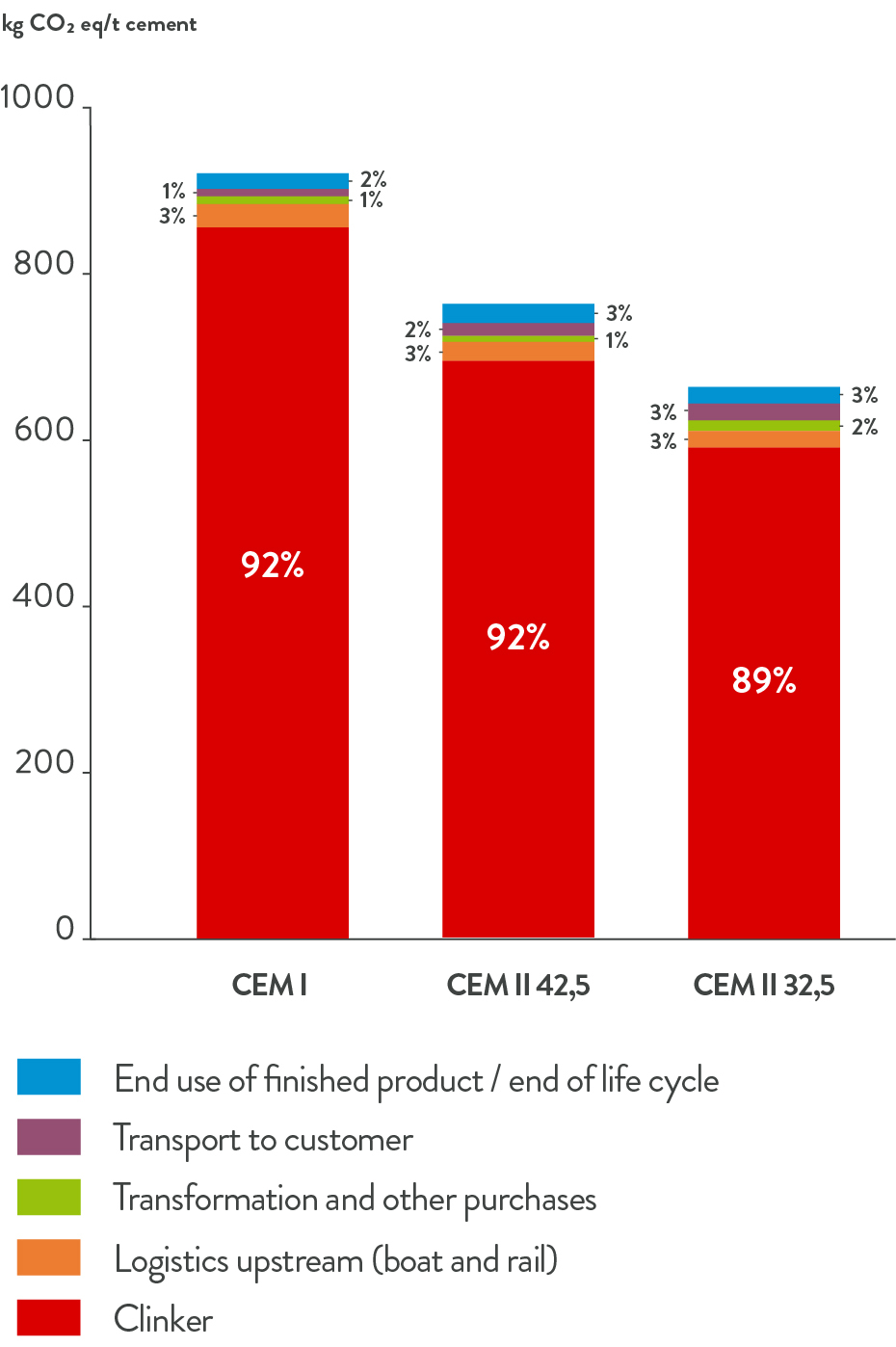
The carbon assessments by cement type:
CEM I 52,5
CEM II 42,5
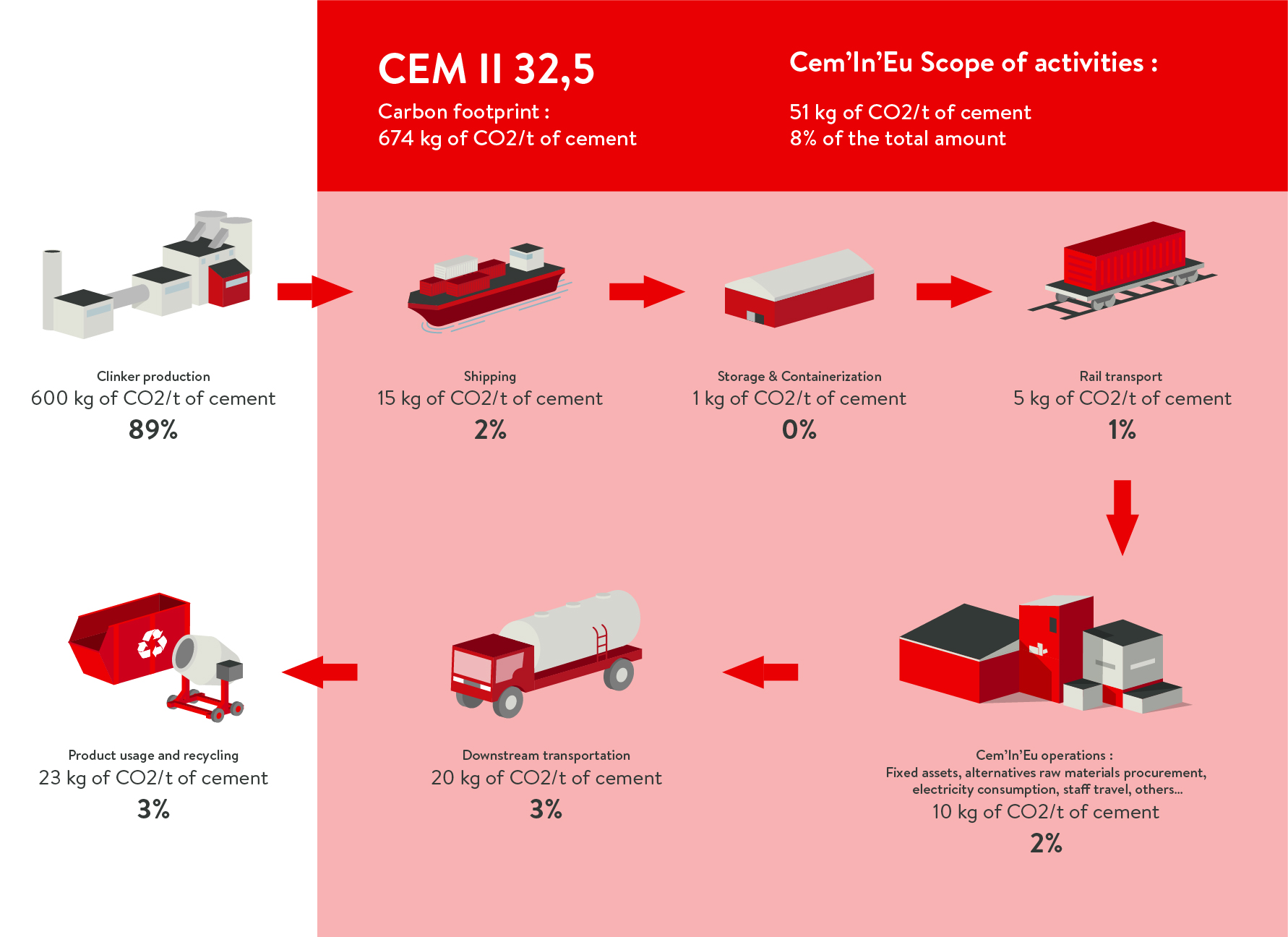
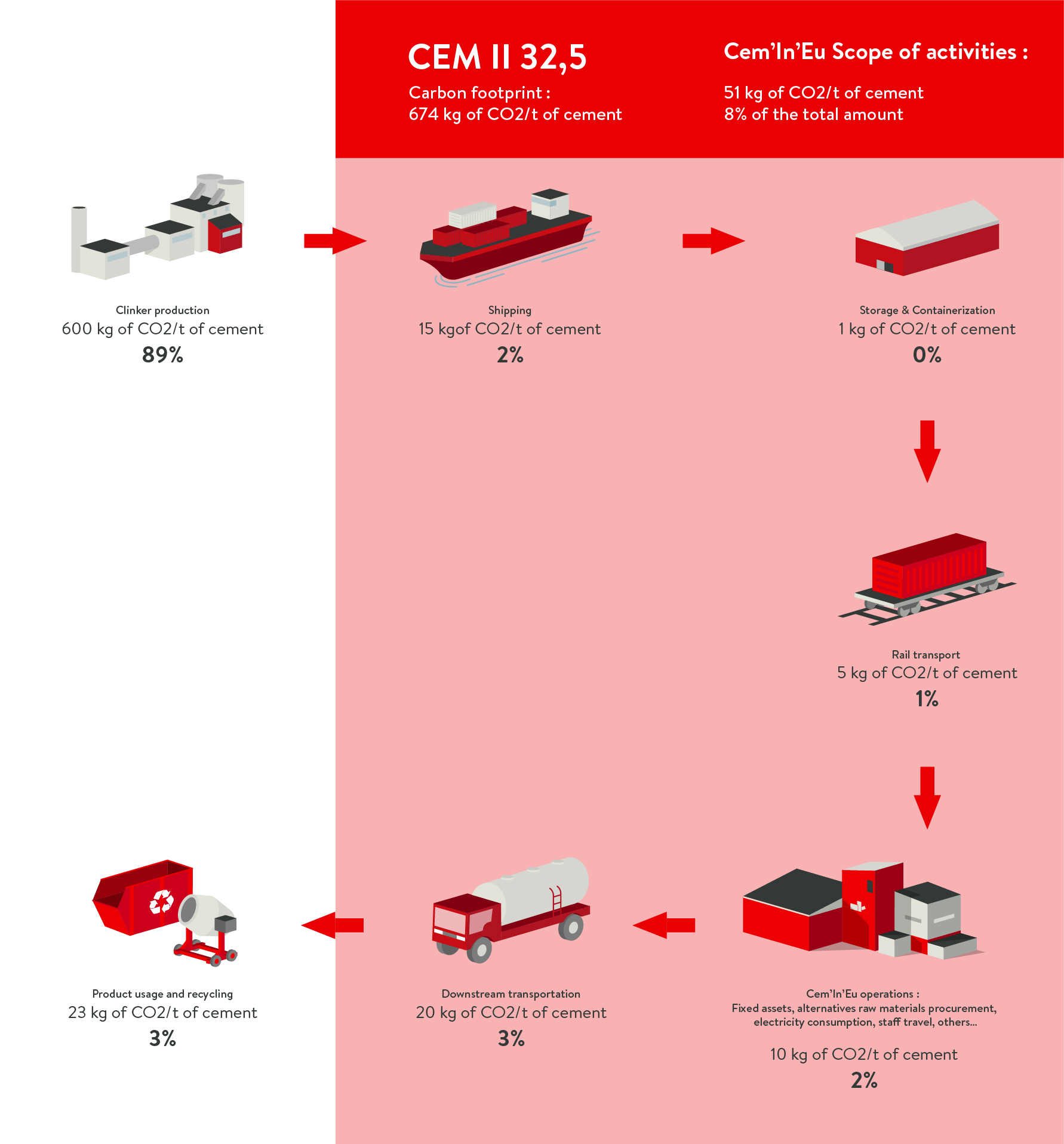
CEM II 32,5
Intervening along the whole value chain
Cem’In’Eu has chosen to act immediately and in a constant manner along all of the stages of the value chain
associated with its areas of operation. There is no such thing as small scale when reducing the carbon footprint, there is
only that which concerns us and upon which we owe to ourselves to act.

Selection of suppliers of clinker
This is carried out based on a multi-criteria concept including the performance of the clinker itself, the energy consumption of the oven (less energy = less CO2), and an optimised logistics in the port in order to reduce the CO2 of maritime transport by a maximum.

Optimised logistics chain
• Acting as true centres of gravity related to their trade catchment areas, the locations of the Cem’In’Eu sites have been chosen so as to reduce the road transport to end customers by the maximum amount.
• A similar thought-process has been instigated on inbound flows, by choosing a multi-modal logistics method concerning notably the sourcing by Aliénor Ciments which is carried out solely by rail, the best performing transport in terms of CO2 emissions per kilometre.
Optimizing energy efficiency of the process
Both downstream and upstream, everything has been put into place to reduce the energy consumption of the industrialised process, as less energy means ultimately less CO2.
Evolution of recipes
The selection of a high performance clinker has allowed Cem’In’Eu to optimise its recipes by substituting a major part of the clinker by other products which are neutral in CO2.

Bagging
For its bagging process Cem’In’Eu has chosen to use recycled and recyclable PE presenting a low carbon footprint, with values that can reach 65% less equivalent CO2, in relation to the same product made from a virgin resin.
Continuous improvement
A carbon footprint reduced by 25% over a year’s activity
Each reduction is to be welcomed and over a year’s activity, the overall cumulative effect can rise quickly. Cem’In’Eu has thus reduced its carbon footprint by 25% simply by optimising all available leveraging possibilities.
A seamless integration into the European Green Deal
The Cem’In’Eu model is in accordance with the European green deal and Cem’In’Eu participates in the debates directed by the European Commission.

The Cem’In’Eu model is in accordance with the European green deal and Cem’In’Eu participates in the debates directed by the European Commission.
• Cem’In’Eu upholds the extension of the European system of exchange of quotas of emissions AND the putting into place of a carbon border adjustment mechanism.
• In order to be equitable and compatible with the WTO, new entrants, including importers may benefit from free quotas on the basis of the benchmark used for the ETS.
• These measures allow for the most innovative actors to be supported and to promote investment in low-carbon solutions.
• To find out more you can discover the public contribution of Cem’In’Eu on the website of the European Commission.